In a significant shift, Google has officially discontinued its cache operator, a move that was initially hinted at back in January when the search giant removed the cache link from its search result snippets. After a nine-month waiting period, users can now confirm that the cache operator is no longer functional. This change follows Google’s recent addition of links to the Wayback Machine, which offers an alternative for users seeking cached versions of web pages.
Why Did Google Remove the Cache Operator?
The decision to eliminate the cache operator seems to be part of a broader strategy by Google. By phasing out the cache feature, Google encourages users to rely on the Wayback Machine for accessing archived web pages. This transition aligns with Google’s ongoing efforts to streamline its search experience and direct users to more reliable sources for historical content.
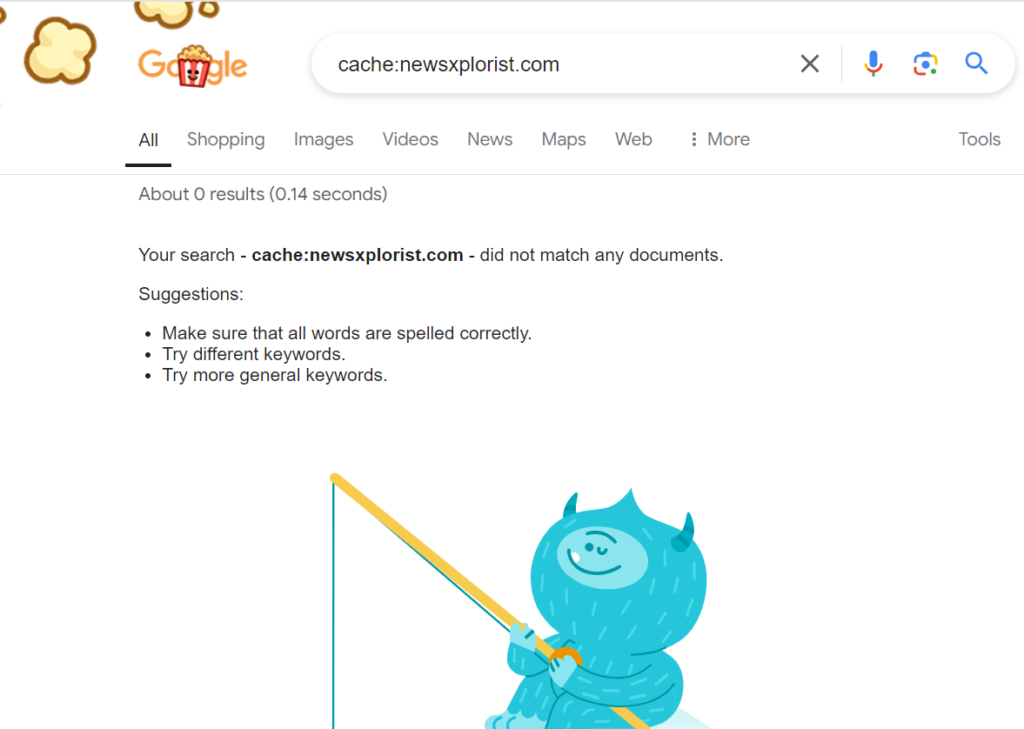
What Does This Mean for Users?
With the cache operator no longer available, users will need to adapt to this change. While the cache feature allowed quick access to older versions of web pages directly through Google search results, the Wayback Machine provides a more comprehensive archive of web pages over time. Users may find the Wayback Machine more useful for detailed historical research or when trying to access information that has since changed or been removed.
FAQs
1. What is the cache operator in Google Search?
The cache operator allowed users to view a saved version of a web page as it appeared when Google last indexed it. This was useful for accessing older content that might have been updated or removed.
2. Why did Google remove the cache feature?
Google removed the cache feature as part of its strategy to enhance the search experience and redirect users to the Wayback Machine, which provides a more robust archival service.
3. What is the Wayback Machine?
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the web, maintained by the Internet Archive. It allows users to access archived versions of web pages dating back to 1996.
4. How can I access old versions of web pages now?
To access archived versions of web pages, users can visit the Wayback Machine website at archive.org/web and enter the URL of the desired page. This will display all the snapshots taken over time. Additionally, if you have access to Google Search Console, you can view the time and date when a page was cached and indexed, providing further context on its historical changes.
5. Will Google provide any alternatives to the cache operator?
While Google has not announced any direct replacements for the cache operator, the addition of the Wayback Machine links serves as a key alternative for users seeking archived content.
Conclusion
The discontinuation of Google’s cache operator marks a significant change in how users access archived web content. By shifting focus to the Wayback Machine, Google is redefining its approach to web archiving and encouraging users to utilize more comprehensive tools for historical research. As we adapt to this change, understanding the new dynamics of accessing information online will be crucial for all users.


Leave a Reply